
| DE / INT: | +49 - (0)36453 - 744-0 | US: | +1 707 4810216 |
| info@layertec.de | ussales@layertec.com |
Bauteile für schwache Nd:YAG oder Nd:YVO4 Laser
Neodymium doped crystals show laser transitions at different wavelengths. Table 1 gives an overview about the laser wavelengths of the most common Nd doped materials Nd:YAG and Nd:YVO4.
| Nd:YAG | Nd:YVO4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser line | Second harmonic | Laser lines | Second harmonic |
| 946 nm | 473 nm | 915 nm | 457 nm |
| 1064 nm | 532 nm | 1064 nm | 532 nm |
| 1123 nm | 561 nm | ||
| 1319 nm | 659 nm | 1340 nm | 670 nm |
| Table 1: | Laser lines and corresponding wavelengths of the second harmonic of Nd:YAG and Nd:YVO4 |
As can be seen, a variety of laser lines in the VIS and NIR can be obtained from these crystals. This phenomenon is used to build compact diode pumped solid stated lasers with a variety of wavelengths which are used for measurement applications as well as for projection systems (RGB lasers).
The strongest laser transition in both materials is the 1064nm line. Efficient laser radiation at the other wavelengths is only possible by suppressing this line. LAYERTEC offers a variety of laser mirrors for this application.
Compact laser designs include also the pump diode (808nm) and a unit for the second harmonic generation. This is the reason, why coatings for Nd:YAG or Nd:YVO4 wavelengths apart from 1064nm mostly show several spectral regions of high transmission as well as of high reflection. In the following we present some examples of such coatings. All coatings are designed according to customer specifications, because the specifications depend on the laser design. All examples on these pages are for Nd:YAG wavelengths. Coatings for Nd:YVO4 can be designed and produced as well.
| Feature | Reflectivity |
|---|---|
| Suppression of the strongest laser line | R(0°, 1064 nm) < 5 % |
| HR mirror for the weak laser line | R(0°, 946 nm) > 99.95 % |
| Higher transmission for the pump wavelength | R(0°, 808 nm) < 2 % |
| HR mirror for the second harmonic of the weak laser line | HR(0°, 473 nm) > 99.85 % |
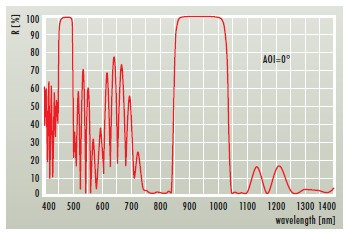
HR(0°, 473nm) > 99.85% + HR(0°, 946nm) > 99.95% + R(0°, 808nm) < 2% + R(0°, 1064nm) < 5%
| Feature | Reflectivity |
|---|---|
| HR mirror for the weak laser line | HR(0°, 1123 nm) > 99.9 % |
| Suppression of the strongest laser line | R(0°, 1064 nm) < 50 % |
| High transmission for the pump wavelength | R(0°, 808 nm) < 10 % |
| High transmission for the second harmonic of the weak laser line | R(0°, 561 nm) < 2 % |
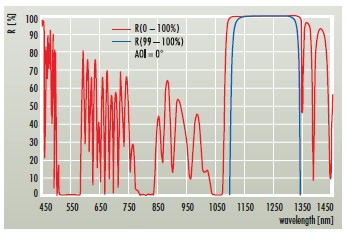
HR(0°, 1123nm) > 99.9% + R(0°, 561nm) < 2% + R(0°, 808nm) < 10% + R(0°, 1064nm) < 50%
| Feature | Reflectivity |
|---|---|
| HR for s-polarized light of the weak laser line | HRs(56°, 1123 nm) > 99.9 % |
| Suppression of p-polarized light of the weak laser line | Rp(56°, 1123 nm) < 50 % |
| Suppression of the strongest laser line | Rs + p(56°, 1064 nm) < 50 % |
| High transmission for the pump wavelength | Rs + p(56°, 808 nm) < 10 % |
| High transmission for the second harmonic of the weak laser line | Rs + p(56°, 561 nm) < 10 % |
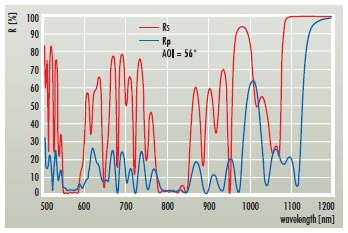
HRs(56°, 1123nm) > 99.9% + Rp(56°, 1123nm) < 50% + Rs,p (56°, 561+808nm) < 10% + Rs,p(56°,1064nm) < 50%
| Feature | Reflectivity |
|---|---|
| Broadband HR mirror for several laser lines | HR(0°, 1064 + 1123 + 1319 nm) > 99.9 % |
| High transmission for the second harmonics of these laser lines | R(0°, 532 - 561 + 659 nm) < 2 % |
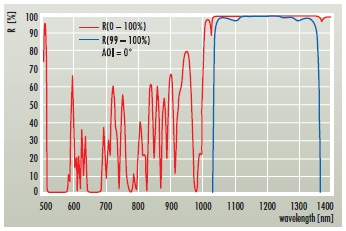
HR(0°, 1064 + 1123 + 1319nm) > 99.9% + R(0°, 532–561+659nm) < 2%
